What is an QCDMS Board?
QCDMS is a comprehensive framework used across industries to assess five key performance areas: Quality, Cost, Delivery, Morale, and Safety. These elements are systematically tracked to promote continuous improvement and support overall operational excellence.
- Quality: Ensuring superior product and service standards through consistent quality checks, defect reduction, and process optimisation to meet or exceed customer expectations.
- Cost: Driving financial efficiency by managing operational expenses, reducing waste, and optimising resource allocation to enhance profitability and maintain budgetary discipline.
- Delivery: Guaranteeing timely and accurate delivery of goods and services by improving logistics, reducing cycle times, and removing process inefficiencies to meet customer demands.
- Morale: Fostering a positive and engaged workforce by encouraging collaboration, supporting professional development, and recognising contributions to boost team performance and satisfaction.
- Safety: Promoting a culture of workplace safety by identifying risks, implementing preventive measures, and complying with safety regulations to ensure employee well-being and operational reliability.
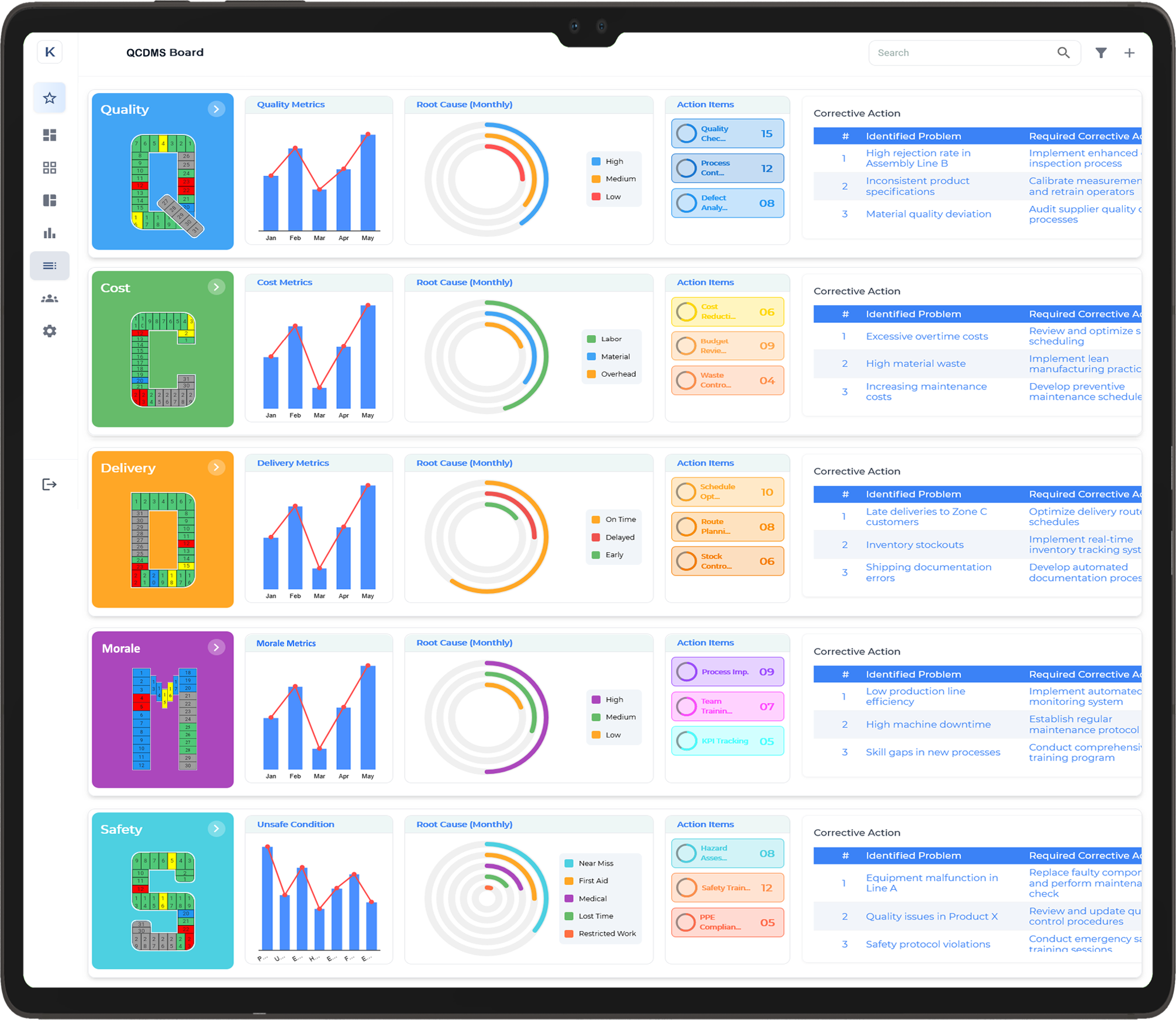
Quality
The Balanced Scorecard’s quality indicators offer a detailed evaluation of product integrity and process performance. By monitoring key aspects such as defect frequency, inspection outcomes, rework activities, and non-conformance documentation—along with supplier and customer feedback—organisations can enhance their quality control systems and drive continuous operational excellence.
- Detected and Assessed Product Defects
- Recorded Failures from Quality Inspections and Functional Testing
- Tracked Rework Cases and Implemented Corrective Measures
- Issued Non-Conformance Reports (NCRs) for Quality Deviations
- Resolved Supplier Material Quality Concerns Effectively
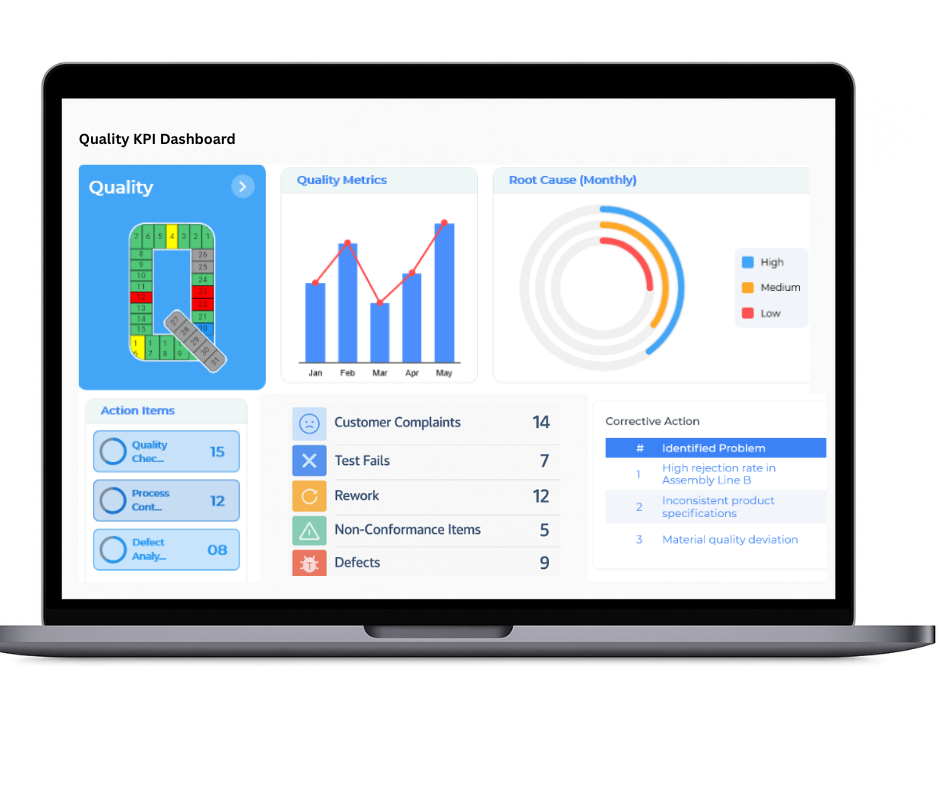
Cost
The Balanced Scorecard plays a critical role in supporting cost management by systematically tracking financial performance and operational efficiency. By analysing key cost drivers and identifying inefficiencies, organisations can uncover opportunities for savings, enforce budgetary discipline, and improve overall profitability.
- Implementation of Cost-Saving Initiatives and Process Improvements
- Tracking of Operational and Departmental Expenditures
- Monitoring Budget Variance and Corrective Action Plans
- Analysis of Resource Utilisation and Waste Reduction Efforts
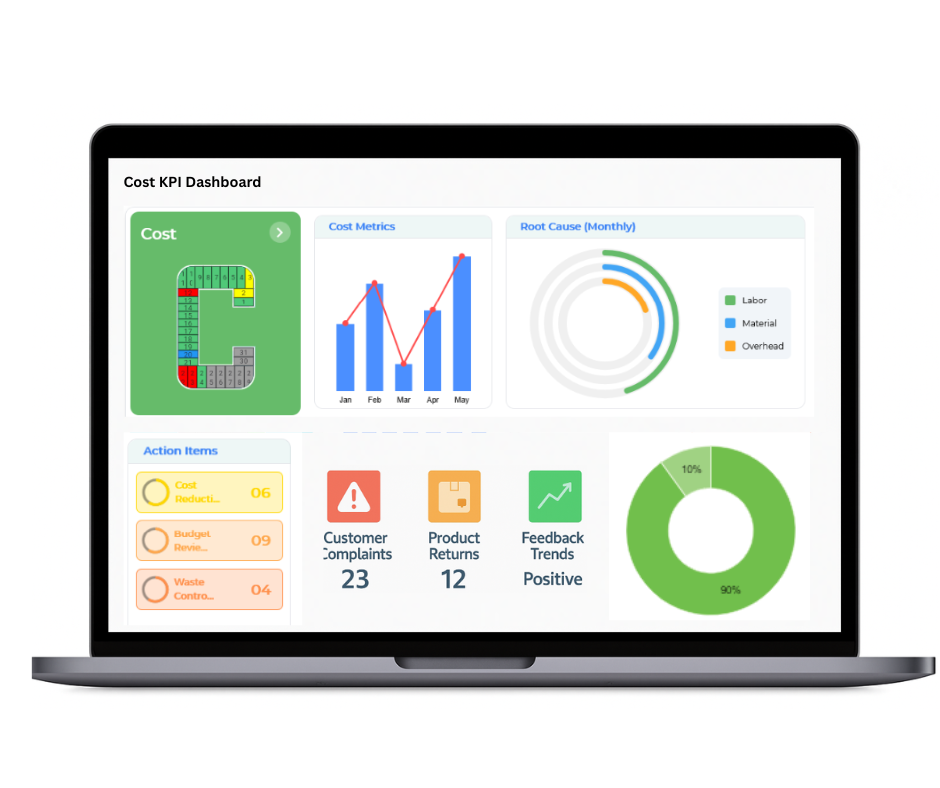
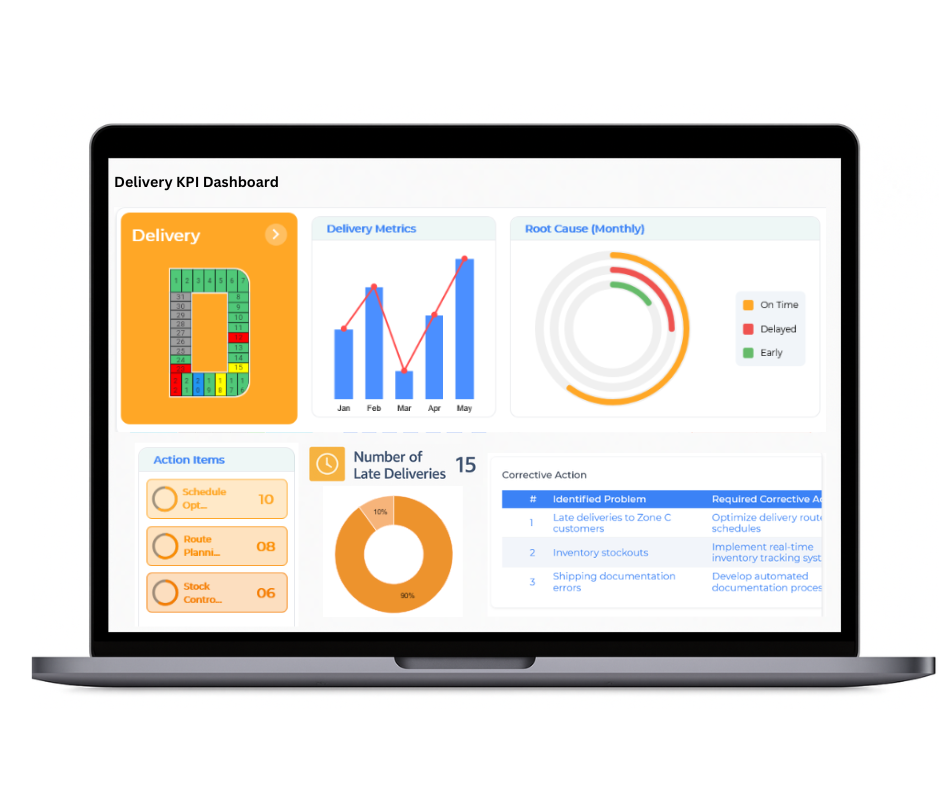
Delivery
The Balanced Scorecard provides a strategic overview of delivery performance, ensuring reliable and timely fulfillment from supplier dispatch to customer receipt. By monitoring logistics operations, accuracy of orders, and inventory movement, it enables teams to identify bottlenecks, streamline processes, and enhance supply chain effectiveness.
- Analysis of Delayed Shipments with Root Cause Investigations
- Measurement of On Time In Full (OTIF) Delivery Metrics
- Verification of Order Fulfillment Accuracy and Consistency
- Assessment of Warehouse Operations and Inventory Cycle Efficiency
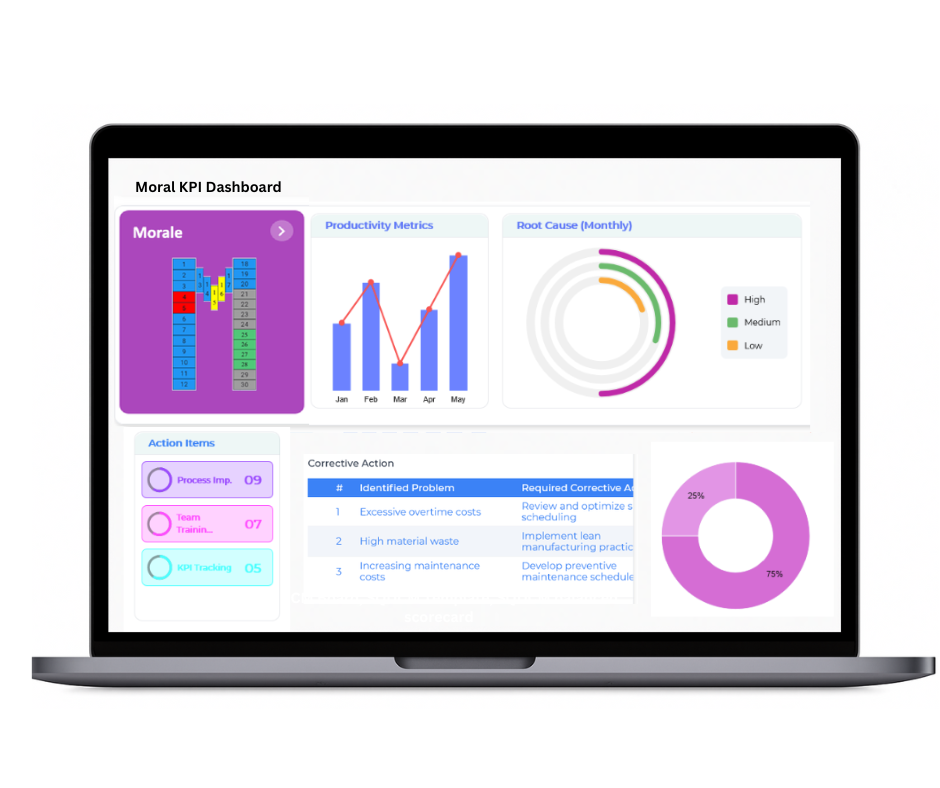
Morale
The Balanced Scorecard plays a key role in nurturing employee morale by systematically tracking engagement, satisfaction, and workforce development. By evaluating feedback, participation, and training effectiveness, organisations can foster a positive work culture, boost motivation, and drive team performance.
- Employee Engagement and Satisfaction Survey Results
- Team Participation in Culture-Building Activities
- Feedback and Recognition Programs Implemented
- Training Sessions and Development Programs Completed
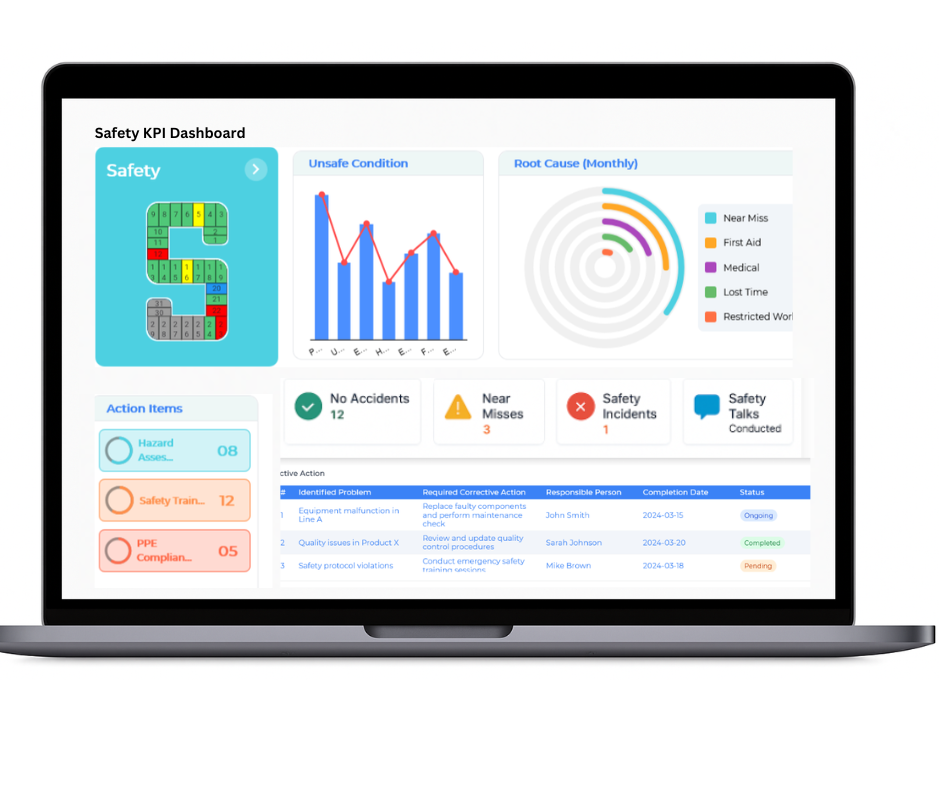
Safety
Safety management is fundamental to fostering a secure and compliant workplace environment. The Balanced Scorecard provides a systematic framework for tracking safety performance, enabling organisations to identify risks, implement preventive measures, and cultivate a proactive safety culture that protects employees and supports operational continuity.
- Implementation of Preventive Safety Measures and Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Ongoing Monitoring of Workplace Safety Incidents and Hazards
- Completion of Safety Audits and Compliance Checks
- Delivery of Safety Training and Awareness Programs
- Continuous Review and Improvement of Safety Protocols
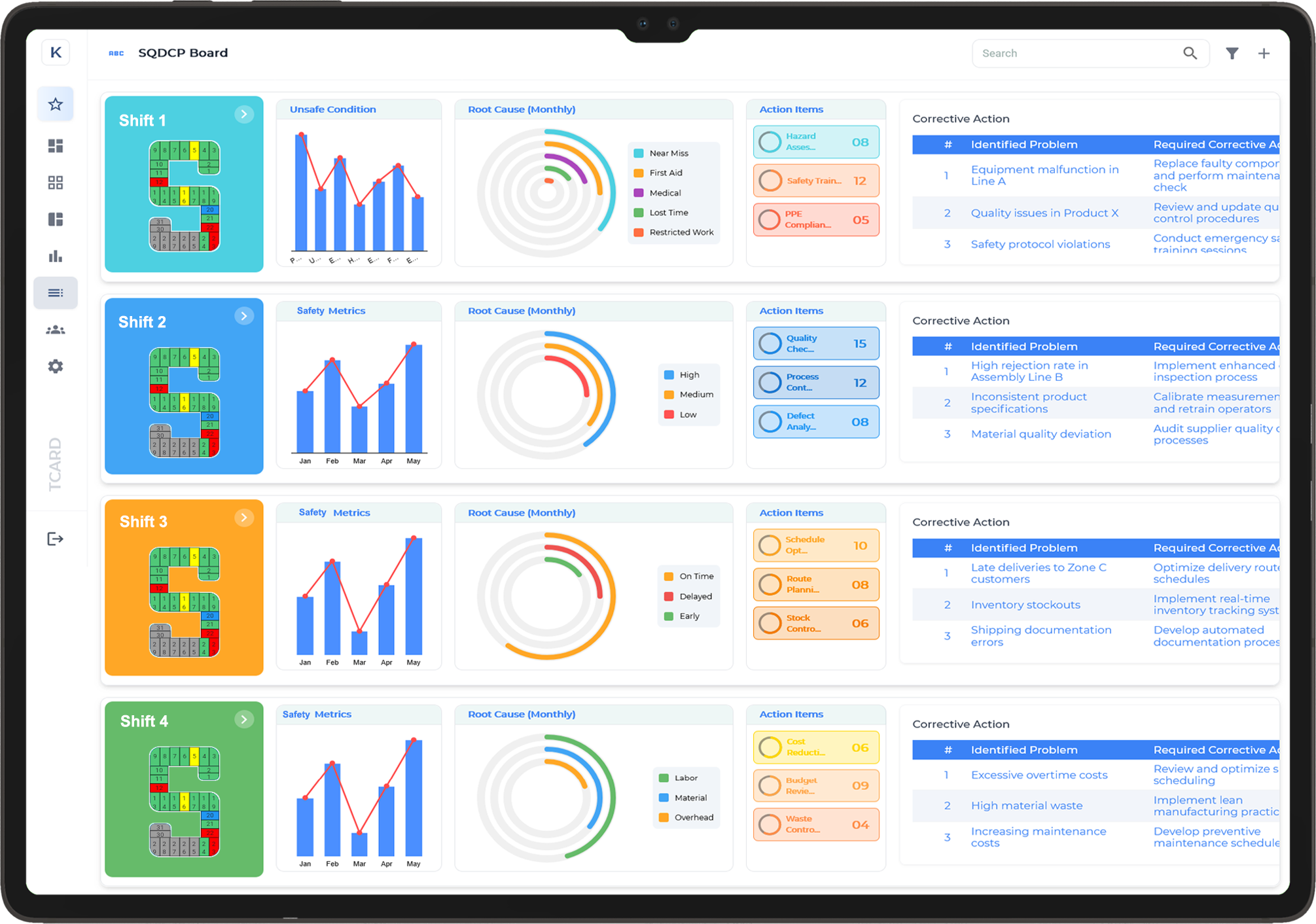
QCDMS Board for Shift Management
- Ongoing Performance Monitoring: Tracks key metrics across Quality, Cost, Delivery, Morale, and Safety to ensure alignment with organisational goals and improve operational outcomes.
- Quality Assurance Focus: Monitors product quality, defect rates, inspection results, and customer feedback to maintain high standards and drive continuous product improvements.
- Cost Control and Efficiency: Tracks operational expenses, identifies areas for cost reduction, and ensures efficient resource allocation to enhance financial performance.
- On-Time Delivery Management: Evaluates delivery performance against target timelines, analyses bottlenecks, and optimises processes to ensure accurate and timely order fulfillment.
- Workforce Morale and Engagement: Measures employee satisfaction, training progress, and overall morale to foster a motivated, collaborative, and productive work environment.
- Safety and Risk Reduction: Continuously monitors safety metrics, tracks incidents and near-misses, and implements risk-reduction strategies to protect employees and maintain a safe work environment.
- Environmental Compliance and Sustainability: Monitors energy use, waste management, and emissions to align with environmental goals and meet regulatory standards.
What Does QCDMS Stand For? Breaking Down the Key Metrics
QCDMS is an acronym that stands for Quality, Cost, Delivery, and Management Systems. These are key performance metrics used to evaluate and improve processes across various industries, particularly in manufacturing and operations. Each metric plays a crucial role in driving efficiency, meeting customer expectations, and enhancing overall business performance.
Quality: Ensuring Consistent Standards
The Quality aspect of QCDMS focuses on the ability to meet or exceed product or service standards. Key metrics might include defect rates, customer complaints, and product returns. By measuring quality, organisations can ensure they are delivering high-value products or services that satisfy customers and minimise waste.
Cost: Managing Expenses Efficiently
Cost is a critical element of QCDMS as it directly impacts profitability. KPIs in this area include production costs, operational expenses, and cost reduction initiatives. By tracking cost metrics, businesses can identify areas where they can reduce waste, improve efficiency, and ultimately increase profit margins.
Delivery: Meeting Deadlines and Customer Expectations
Delivery measures how effectively an organisation meets customer demands within agreed timeframes. Key metrics for delivery might include on-time delivery rates, lead time, and order accuracy. By focusing on delivery, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty while improving operational flow.
Management Systems: Optimising Organisational Processes
Management Systems in QCDMS focus on the systems and processes in place to manage operations. This includes metrics related to process efficiency, compliance, and continuous improvement. Effective management systems ensure that quality, cost, and delivery metrics are optimised and aligned with business goals.
QCDMS is a comprehensive approach to evaluating performance. By focusing on these key metrics, businesses can improve their operations, deliver higher-quality products, and enhance customer satisfaction.
The Role of QCDMS Boards in Lean Manufacturing
QCDMS boards are a vital tool in lean manufacturing, helping businesses streamline operations and improve overall performance. QCDMS stands for Quality, Cost, Delivery, and Management Systems, and these metrics play a crucial role in identifying inefficiencies and driving continuous improvement within manufacturing environments.
Quality: Consistency and Process Improvement
In lean manufacturing, quality is a primary focus. QCDMS boards allow teams to track and visualise quality metrics, such as defect rates and product returns. This visibility helps identify areas where quality can be improved, reduce rework, and ultimately lead to fewer defects and higher customer satisfaction. Consistent product quality is a key component of lean practices.
Cost: Reducing Waste and Improving Efficiency
One of the central principles of lean manufacturing is waste reduction. By using QCDMS boards, teams can closely monitor cost-related metrics, such as production expenses, energy usage, and raw material costs. These boards provide valuable insights that help businesses identify opportunities to cut costs, optimise resources, and eliminate waste from the production process.
Delivery: Meeting Customer Expectations
Meeting deadlines and delivering products on time is critical for customer satisfaction in lean manufacturing. QCDMS boards help track delivery performance by measuring key metrics like on-time delivery and lead times. This real-time tracking enables teams to identify bottlenecks, address delays, and ensure that customer demands are met efficiently.
Management Systems: Streamlining Operations
Management Systems in lean manufacturing ensure that all processes are aligned and running smoothly. QCDMS boards help monitor key operational processes, enabling teams to spot inefficiencies and implement corrective actions. These systems promote a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring that all aspects of manufacturing contribute to the overall lean strategy.
QCDMS boards are essential for achieving lean manufacturing goals. By providing a clear visual representation of quality, cost, delivery, and management system metrics, they enable teams to make data-driven decisions that lead to more efficient and effective manufacturing processes.
How QCDMS Boards Help Improve Quality Control Across Teams
QCDMS boards play a significant role in improving quality control across teams by providing clear and actionable insights into key metrics. By focusing on Quality, Cost, Delivery, and Management Systems, QCDMS boards help ensure that teams are aligned and working towards continuous improvement. When integrated into daily operations, they help organisations maintain high-quality standards and enhance overall productivity.
Real-Time Quality Monitoring
One of the most powerful features of QCDMS boards is their ability to provide real-time monitoring of quality metrics. Teams can easily track product defects, customer feedback, and inspection results. This visualisation of quality data allows for immediate action, preventing small issues from escalating into bigger problems. By constantly monitoring quality, teams can quickly identify areas of improvement and implement corrective actions before defects affect customers.
Root Cause Analysis and Continuous Improvement
QCDMS boards not only highlight quality issues but also support root cause analysis. With data visualisation, teams can easily identify recurring problems and their underlying causes. This information is critical for implementing long-term solutions. By continuously tracking quality metrics and addressing the root causes of defects, teams contribute to a culture of continuous improvement, which is key to maintaining high-quality standards across all operations.
Cross-Team Collaboration and Accountability
QCDMS boards promote collaboration across different teams by making quality metrics visible and accessible. When quality performance is displayed on the board, everyone involved—whether in production, maintenance, or management—can see how their work impacts the overall quality. This shared visibility fosters accountability, encourages teamwork, and helps teams work together to meet quality goals.
QCDMS boards are invaluable tools for improving quality control across teams. They enable real-time monitoring, root cause analysis, and enhanced collaboration, all of which contribute to maintaining high-quality standards and driving continuous improvement.
Managing Costs Effectively with QCDMS Boards
QCDMS boards provide a clear and effective way to manage costs across various operations. By tracking key metrics such as production expenses, material costs, and waste reduction, these boards offer valuable insights that help organisations identify areas for cost savings. Through regular monitoring and data visualisation, teams can make informed decisions that optimise resources and reduce unnecessary expenditures.
Tracking Operational Costs in Real Time
One of the main advantages of using QCDMS boards is the ability to track operational costs in real time. By displaying cost metrics on the board, teams can immediately see how their activities impact the overall budget. Whether it’s tracking the cost of raw materials, labour, or energy, QCDMS boards ensure that cost data is always up to date. This visibility allows for prompt adjustments to be made, helping to keep costs under control.
Identifying Areas for Cost Reduction
QCDMS boards make it easy to identify areas where costs can be reduced. By analysing the data displayed, teams can spot inefficiencies and waste in processes. For instance, if material usage is higher than expected, the team can investigate and take corrective actions. By focusing on cost-saving initiatives, such as minimising waste or improving labour efficiency, organisations can significantly reduce operational expenses.
Improving Budget Forecasting
With QCDMS boards, teams gain better visibility into their cost trends, which can improve future budget forecasting. By analysing historical cost data, organisations can predict upcoming expenses more accurately and make adjustments to stay within budget. This proactive approach helps to avoid surprises and ensures financial stability in the long run.
Boosting On-Time Delivery Performance with QCDMS Tracking
On-time delivery is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. QCDMS boards offer a powerful tool for tracking delivery performance and ensuring that deadlines are consistently met. By visualising key delivery metrics such as order fulfilment rates, lead times, and delays, QCDMS tracking helps organisations identify issues and improve their delivery processes.
Real-Time Delivery Monitoring
QCDMS boards provide real-time tracking of delivery performance, allowing teams to monitor progress at each stage of the process. By displaying metrics such as delivery deadlines, current order status, and potential delays, teams can stay informed and take action as needed. This instant visibility helps identify any bottlenecks that may hinder timely deliveries, enabling proactive intervention to stay on track.
Improving Process Efficiency
With QCDMS tracking, organisations can pinpoint inefficiencies in the delivery process. Whether it’s delays in production, issues with inventory, or transportation hold-ups, the board helps highlight the root causes of delivery failures. By addressing these inefficiencies, teams can streamline operations, reduce delays, and improve overall delivery performance. Continuous monitoring allows teams to make adjustments and improve speed without compromising quality.
Enhancing Communication Across Teams
QCDMS boards foster improved communication across teams by providing a centralised platform for delivery tracking. Whether it's the production team, logistics, or customer service, everyone can access up-to-date delivery data. This shared visibility ensures alignment and helps all departments work together to meet delivery deadlines. Improved communication helps prevent delays caused by miscommunication or missed updates.

The Importance of Safety Metrics on a QCDMS Board
Safety is a top priority in any workplace, and monitoring safety performance is essential for maintaining a secure environment. A QCDMS board provides an effective way to track and visualise safety metrics, ensuring that organisations stay focused on preventing accidents and improving overall workplace safety. By displaying key safety data, teams can spot potential hazards and take immediate action to address issues before they escalate.
Tracking Safety Incidents
Safety incidents, including accidents, injuries, and near misses, should be closely monitored to identify trends and prevent future occurrences. QCDMS boards allow for the real-time tracking of these incidents, enabling teams to understand where issues are most likely to occur. By visualising incident data, organisations can identify high-risk areas and implement targeted strategies to improve safety, reducing the risk of harm to employees.
Promoting a Safety Culture
Displaying safety metrics on a QCDMS board encourages a safety-first mindset among employees. When safety data is visible to everyone, it creates awareness and keeps safety top of mind throughout the day. It also fosters accountability, as teams can see how their actions impact safety outcomes. Regular updates on safety metrics, such as the number of days without accidents, motivate employees to maintain safe practices and strive for continuous improvement.
Supporting Compliance and Reporting
QCDMS boards help organisations stay compliant with safety regulations by tracking essential safety data required for reporting. This ensures that organisations meet legal requirements and are prepared for audits. By keeping safety metrics updated and easily accessible, teams can streamline the reporting process and demonstrate a commitment to maintaining a safe working environment.
Integrating QCDMS Boards with Your Daily Operations
Integrating QCDMS boards into daily operations is a powerful way to streamline processes and enhance performance across various departments. By tracking critical metrics such as Quality, Cost, Delivery, Manufacturing, and Safety (QCDMS), organisations can ensure better decision-making and improve overall efficiency. These boards offer real-time visibility, enabling teams to focus on key areas that drive success.
Real-Time Monitoring of Key Metrics
One of the biggest advantages of using QCDMS boards is the ability to monitor essential performance metrics in real time. By tracking quality, cost, delivery, and safety data on a single board, teams can identify potential issues early and make informed decisions. This proactive approach helps teams stay on top of problems before they affect productivity, ensuring smooth operations throughout the day.
Aligning Teams Around Common Goals
QCDMS boards help create alignment within teams by clearly displaying key performance indicators (KPIs) that everyone can track and work towards. Whether it’s maintaining product quality, meeting delivery timelines, or reducing costs, the metrics on the board help keep everyone focused on the same objectives. This transparency fosters collaboration and accountability, empowering teams to take ownership of their results and work together to improve performance.
Driving Continuous Improvement
Integrating QCDMS boards into daily operations fosters a culture of continuous improvement. By constantly reviewing and updating performance metrics, organisations can identify areas for optimisation and implement corrective actions where necessary. This ongoing feedback loop helps teams make incremental improvements that add up to significant gains in overall efficiency and productivity.
Digital vs Physical QCDMS Boards: Which Works Best for Your Team?
When choosing between digital and physical QCDMS boards, it’s essential to consider the needs of your team and the specific environment in which you operate. Both options offer distinct advantages, but each may be more suitable depending on your team’s workflow, location, and resources.
Advantages of Digital QCDMS Boards
Digital QCDMS boards offer several benefits that can enhance real-time communication and data accuracy. They allow for seamless integration with other software tools, providing a comprehensive view of performance metrics across multiple teams or locations. Updates can be made instantly, ensuring that all team members are on the same page. Digital boards also provide valuable data analytics, which can help track trends over time, identify potential issues, and measure improvement efforts.
Benefits of Physical QCDMS Boards
Physical QCDMS boards, on the other hand, offer a tactile and visual representation that can be particularly useful in manufacturing or service environments. They provide a clear, immediate view of key performance indicators, which can be accessed by anyone on the floor. Physical boards can also encourage engagement and communication, as team members can physically update the board, add notes, or visually track progress during daily stand-up meetings. They are a great option for teams that prefer a more hands-on, low-tech solution.
Which Is Right for Your Team?
The choice between digital and physical QCDMS boards depends on factors such as your team's size, technical proficiency, and operational complexity. If your team is dispersed across multiple locations or if you require sophisticated data analysis, digital boards might be the best choice. Conversely, if you have a smaller team or work in a hands-on environment where physical visibility is crucial, a physical QCDMS board might be more effective.
Ultimately, the right choice will depend on your unique team dynamics and operational goals. Combining both digital and physical boards is also an option that many teams use to maximise the benefits of each.
Customising QCDMS Boards to Fit Your Unique Business Needs
Customising your QCDMS board is crucial for ensuring it aligns with your business's specific goals and processes. Whether you’re in manufacturing, services, or any other sector, a tailored QCDMS board can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance team communication. Here’s how to make it work for your business.
Tailoring Metrics to Your Business Priorities
The first step in customising a QCDMS board is selecting the right key performance indicators (KPIs). These should reflect your organisation's unique objectives. For example, if quality control is a top priority, you can emphasise quality-related metrics, such as defect rates or customer satisfaction scores. Similarly, if cost reduction is a key focus, make sure cost-efficiency metrics are front and centre.
Customising Visuals for Clarity
Customisation also extends to the visual elements of your QCDMS board. Colour coding, charts, and graphs can be adapted to your team’s preferences, making it easier to quickly identify areas that need attention. For instance, using red to signal critical issues and green for performance on target can instantly communicate the status of different areas at a glance. Customising these visuals ensures that all team members can interpret the board effectively without confusion.
Incorporating Your Team’s Input
Your QCDMS board should also reflect the needs and preferences of the people using it. Get input from team members on what information they need most frequently and how they prefer to receive it. This collaboration ensures the board is not only a tool for management but also a resource that supports team engagement and performance improvement.
By customising your QCDMS board, you create a solution that is perfectly suited to your business’s goals, workflows, and team dynamics, enhancing overall productivity and focus.
Tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) on a QCDMS Board
Tracking Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) on a QCDMS board is essential for monitoring the performance of various areas within your organisation. KPIs provide measurable insights into your business's operations, helping teams stay aligned with goals and identify areas for improvement. Here's how to effectively track KPIs on your QCDMS board.
Selecting the Right KPIs
The first step in tracking KPIs is selecting the right metrics that align with your business goals. For a QCDMS board, key areas to focus on include Quality, Cost, Delivery, and Safety. Choose KPIs that reflect the most critical aspects of your operations, such as defect rates for quality, cost savings for cost management, on-time delivery rates, and accident rates for safety.
Making KPIs Visual and Accessible
Once you have selected the KPIs, make them visually engaging and easy to understand on your QCDMS board. Use colour-coded charts, graphs, and progress bars to represent the current status of each KPI. This helps team members quickly assess performance at a glance. For example, red can indicate areas requiring immediate attention, while green shows that performance is on target.
Regularly Updating and Reviewing KPIs
To ensure your QCDMS board is effective, regularly update the KPIs and review them in team meetings. Set clear targets and track progress consistently to stay on top of any challenges. This not only fosters transparency but also enables proactive decision-making to improve overall performance.
Tracking KPIs on a QCDMS board helps ensure everyone is focused on the right priorities, fostering continuous improvement and better decision-making across teams.
Real-Time Data on QCDMS Boards: Driving Quick Decision-Making
Real-time data on QCDMS boards plays a pivotal role in driving swift and informed decision-making. By offering instant access to key metrics, teams can react promptly to issues, optimise performance, and ensure that operations run smoothly. Here's how real-time data enhances decision-making on QCDMS boards.
Instant Access to Critical Information
One of the main benefits of using real-time data on a QCDMS board is the ability to access up-to-date information at any moment. Whether it's tracking production speed, safety incidents, or cost performance, real-time data ensures that teams have the latest insights at their fingertips. This eliminates delays and helps prevent costly mistakes by enabling quick actions based on the most current data.
Quick Identification of Issues
With real-time updates, problems can be spotted immediately. For example, if a production line experiences a delay, the team can address the issue before it affects delivery schedules. Real-time monitoring of quality, cost, and safety helps prevent minor issues from escalating into major setbacks, ensuring that resources are used efficiently and goals are met on time.
Improved Collaboration and Response
Real-time data fosters better communication across departments. With clear visibility of performance metrics, team members can collaborate more effectively and make decisions quickly. This transparency leads to quicker problem resolution and smoother workflows across all areas of the organisation.
Incorporating real-time data into your QCDMS board ensures that decision-makers are always informed, improving overall efficiency and boosting the organisation’s ability to adapt to changes swiftly.
How QCDMS Boards Foster Cross-Department Collaboration
QCDMS boards are an essential tool for promoting cross-department collaboration. By centralising key metrics such as quality, cost, delivery, and safety, these boards provide a unified platform where all departments can align their efforts. Here’s how QCDMS boards facilitate better teamwork across your organisation.
Unified Visibility for All Teams
QCDMS boards offer a transparent view of key performance indicators (KPIs) for every department involved in production, from manufacturing to logistics. With all critical data displayed in one place, teams can quickly identify how their work contributes to overall goals. This shared visibility promotes a collaborative mindset, encouraging departments to work together toward achieving organisational objectives.
Improved Communication and Problem Solving
When issues arise, such as delays in production or safety concerns, QCDMS boards allow all relevant teams to see the problem in real time. This enables swift discussions between departments to find effective solutions. The ability to visualise the situation makes it easier to understand the root causes and take coordinated action quickly, ensuring minimal disruption to operations.
Enhanced Accountability and Ownership
With clear metrics displayed on QCDMS boards, each department becomes more accountable for its performance. Teams are more likely to take ownership of their KPIs, knowing that their results are visible to others. This shared responsibility fosters a culture of collaboration, as departments strive to meet their targets while supporting others in achieving theirs.
By promoting visibility, communication, and accountability, QCDMS boards help break down silos and create a more collaborative, efficient workplace.
Best Practices for Setting Up a QCDMS Board in Your Organisation
Setting up a QCDMS board in your organisation can significantly improve transparency and decision-making. To ensure its effectiveness, follow these best practices to make the most of this powerful tool.
1. Define Clear Objectives and KPIs
Before setting up your QCDMS board, it’s essential to define the objectives and key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be tracked. These should align with your organisation’s goals, such as improving quality, reducing costs, or enhancing delivery times. Choose KPIs that are measurable and relevant to your team's performance.
2. Keep It Simple and Focused
A cluttered QCDMS board can overwhelm users and reduce its effectiveness. Keep the layout simple and focused on the most important metrics. Use clear labels and colour coding to differentiate between categories like quality, cost, delivery, and safety, making it easy for everyone to understand at a glance.
3. Update Regularly
For the QCDMS board to be effective, it must be updated regularly. Set a routine for updating metrics, whether daily, weekly, or after each shift. This ensures that the board reflects current performance and helps teams make real-time decisions based on up-to-date data.
4. Involve the Entire Team
Engage all relevant departments in the setup and maintenance of the QCDMS board. Involving employees in tracking and reviewing metrics fosters a sense of ownership and encourages them to take responsibility for their performance. Collaboration leads to better outcomes.
5. Use Visuals for Clarity
Visual elements such as charts, graphs, and colour coding can make data more accessible and easier to understand. A visual QCDMS board allows everyone to quickly grasp the status of key metrics and identify areas for improvement.
By following these best practices, you can ensure your QCDMS board is an effective tool for driving improvement, increasing accountability, and aligning team efforts towards common goals.
How QCDMS Boards Support Continuous Improvement and Problem-Solving
QCDMS boards are powerful tools that foster continuous improvement and problem-solving in an organisation. By visualising key performance metrics such as quality, cost, delivery, and safety, these boards help teams identify issues, track progress, and make data-driven decisions to drive improvement.
1. Real-Time Visibility for Quick Problem Identification
QCDMS boards provide real-time visibility into operational performance, allowing teams to quickly identify issues as they arise. For example, if delivery times are slipping or quality is decreasing, the team can take immediate action to address the problem before it escalates. This visibility promotes a proactive approach to problem-solving, which is vital for continuous improvement.
2. Data-Driven Decision-Making
By tracking key metrics and displaying them on a QCDMS board, organisations can make data-driven decisions. Having access to accurate, up-to-date data helps teams identify patterns, root causes, and areas of inefficiency. With this information, managers can guide problem-solving efforts and implement targeted improvements, resulting in more efficient processes.
3. Facilitating Team Collaboration
QCDMS boards are a central point for team collaboration. During meetings, teams can review the board together, discuss challenges, and brainstorm solutions. This collaborative approach fosters a culture of continuous improvement, where everyone is invested in problem-solving and finding ways to enhance performance.
4. Tracking Improvements Over Time
With QCDMS boards, improvements are clearly visible. As changes are implemented, teams can monitor the effects on key metrics over time. This tracking allows teams to celebrate successes, adjust strategies where necessary, and ensure that continuous improvement efforts are consistently yielding positive results.
By leveraging QCDMS boards, organisations can create a systematic approach to problem-solving and continuous improvement, driving long-term success.
Case Studies: Companies That Have Transformed Operations with QCDMS Boards
Many organisations have successfully transformed their operations using QCDMS boards. These boards, which track quality, cost, delivery, and safety metrics, provide a clear overview of performance, helping teams to drive continuous improvement. Below are a few real-world examples of how companies have benefited from QCDMS boards.
1. Enhancing Operational Efficiency in Manufacturing
A leading manufacturing company implemented QCDMS boards to track their production line performance. By visualising real-time data on quality, cost, and delivery, the company quickly identified inefficiencies and areas where improvements were needed. The boards allowed them to streamline processes, reduce costs, and improve delivery times, leading to a significant increase in overall efficiency. With clear, actionable insights, managers were able to make informed decisions, which resulted in enhanced productivity and reduced waste.
2. Improving Quality Control in the Service Industry
A service-based business adopted QCDMS boards to monitor customer satisfaction, service delivery, and operational costs. By using the board to track these metrics, they identified trends in customer feedback, pinpointing areas where quality could be improved. The team quickly responded to emerging issues, implementing new service protocols that led to higher customer satisfaction and reduced operational costs. The QCDMS board empowered staff to monitor quality consistently and maintain high standards of service.
3. Strengthening Safety and Compliance in Construction
In the construction industry, safety is paramount. A construction company implemented QCDMS boards to monitor safety metrics and ensure compliance with industry standards. The real-time tracking of safety incidents and near-misses allowed the company to quickly address any hazards, reducing the risk of accidents and ensuring a safer work environment. The board became a valuable tool for fostering a safety-first culture and improving compliance across all projects.
These case studies demonstrate the transformative power of QCDMS boards in various industries. By visualising key metrics, organisations can make better decisions, improve performance, and create a culture of continuous improvement.
Benefits of QCDMS Board
QCDMS boards are a powerful tool for organisations looking to improve operational efficiency. These boards allow teams to visually track key metrics related to quality, cost, delivery, manpower, and safety (QCDMS). The benefits they offer are substantial, making them an essential asset in any business striving for continuous improvement.
1. Improved Decision-Making
By providing real-time, visual data, QCDMS boards allow decision-makers to quickly identify areas needing attention. Whether it's a dip in quality or a rise in costs, having clear metrics helps managers make informed decisions faster, enabling timely corrective actions that keep operations on track.
2. Enhanced Communication and Collaboration
QCDMS boards improve communication within teams by displaying up-to-date information in an easily accessible format. This transparency encourages collaboration between departments, ensuring everyone is aligned and working towards the same goals. Whether in manufacturing or service-based industries, this shared visibility fosters a sense of accountability and teamwork.
3. Streamlined Performance Monitoring
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) on a QCDMS board simplifies performance monitoring. Teams can easily track progress, set goals, and review historical data, which supports continuous improvement. With a visual representation of metrics, employees at all levels can quickly understand the state of operations, enabling quicker responses to challenges.
4. Increased Focus on Safety and Compliance
Safety is a critical metric in many industries, and QCDMS boards make it easier to track safety incidents and compliance. By regularly monitoring safety data, organisations can take proactive steps to minimise risks, ensuring a safer work environment and reducing the likelihood of accidents.